The PHR Framework
This section provides a conceptual overview of the ABDM federated health record framework. Read this to understand how various building blocks of ABDM works and where your application fits in this ecosystem.
- Electronic Health Records
- Health Facility Registry (HFR) for facility identity
- What is a Health Information Provider (HIP)?
- What is a Health repository Provider (HRP)?
- Identifying patients via ABHA address
- Use ABHA number for patients without phones
- Health Information Exchange & Consent Manager
- Capturing ABHA address during patient registration
- Linking of records by HRP / HIP
- Discovery of records by patients
- Federated Health Records Architecture
- PHR applications & Health Lockers
- What are Health Information Users (HIUs)
- Sharing Health records with consent
- HIP / HIU Guidelines
- HDCM Policy
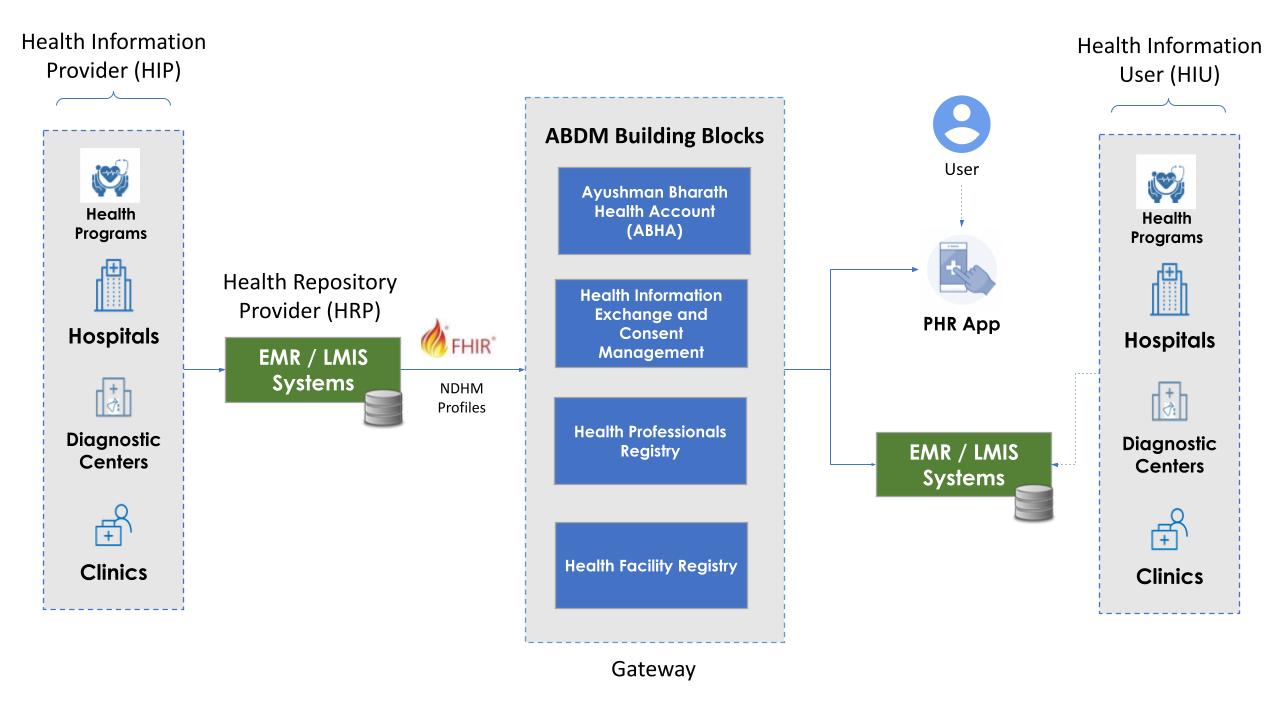
ABDM uses a federated health record (FHR) framework that allows users (patients) to collect their health records across various healthcare providers, view their records from any Personal Health Record (PHR) application and share their records with their consent
The image below shows the various entities/roles involved in the FHR framework
Electronic Health Records
Electronic Health records are digital records that are created by Health service providers as part of their interactions with patients. Health Providers use specialized software called electroic medical record (EMR), health information management systems (HIMS) or Lab information management systems (LIMS) to create these health records.
Health records include Diagnostic reports, discharge summaries, prescriptions, OP consultation notes, etc. The ABDM FHR framework deals with the format of health records (to enable interoperability), the storage of health records (to ensure they are available) and the sharing of health records with consent. Every Health record contains information about who is the patient, which health professional provided the treatment and at which facility. ABDM requires each of these entities to obtain a digital identifier and use that identifer when creating / linking health records under ABDM.
Health Facility Registry (HFR) for facility identity
Health Facilities are issued a HFR ID when their register their facility with ABDM. They can register via https://facility.abdm.gov.in. Digital Solution Companies can also help their customers register with HFR within their software by integrating with the HFR APIs.
What is a Health Information Provider (HIP)?
Any entity that agrees to share digital health records with their users using the ABDM APIs is called an HIP (Health Information Provider). HIPs can be hospitals, labs, health care centers, government health programs, teleconsultation players, clinics or pharmacies - basically any entity which creates medical data pertaining to a patient. The HFR ID is used to identify which facility has agreed to become a HIP and is sharing health information. (HFR ID == HIP ID)
HIPs are required to maintain a digital copy of both the inpatient and outpatient records for each person in their care. They also need to adhere to the HIP HIU Guidelines
HIPs are eligible for financial incentives under the ABDM Digital Health Incentive Scheme
What is a Health Repository Provider (HRP)?
Health repository providers are digital solution companies who offer ABDM compliant software to health facilities like hospitals, diagnostic centers etc. An instance of an ABDM certified software is a HRP. The HRP enables healthcare providers to become HIPs or HIUs and meet their obligations of sharing and securely maintaining health records of patients digitally. HRPs offer long term storage of health records on behalf of a HIP. For example, a hosted lab information management system provider (LIMS) may update their software to become a ABDM compatible Health Repository Provider. Any lab using this hosted LIMS software can rapidly become a HIP by adopting the software.
The ABDM sandbox hosts a reference HRP – You can play with it at https://emrsbx.abdm.gov.in
Identifying patients via ABHA address
In order to manage their personal health records, users (patients) must first create an account on a HIE-CM – called their Ayushman Bharath Health Account (ABHA) address. This looks like sandeep321@abdm. The @abdm tells us which HIE-CM is responsibile for this address.
The term ABHA address is also reffered to as PHR address across the documentation
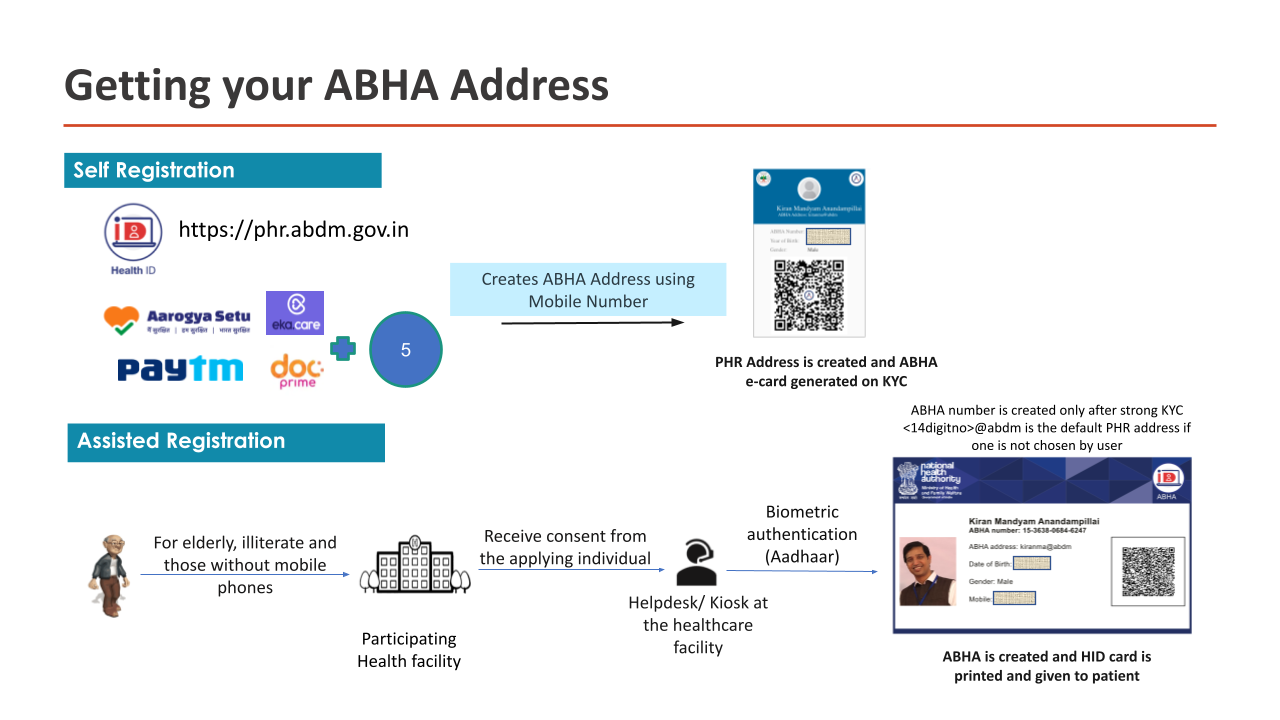
Hospitals & Labs are expected to link records with their patients ABHA Address. Creating an ABHA Address is super simple – You can start with just Name, Year of birth, Gender along with a Mobile number. ABHA address can be linked to a strongly validated & unique ABHA Number
ABDM is designed to work for people with smartphones, features phones and even those without phones. Users with smartphones can be encourgaed to get their ABHA address via a PHR app. They can create a easy to remember ABHA address that is alphanumeric like sandeep321@abdm. Users with only feature phones or without phones will require assitance in creating an ABHA address. It is recommended that they create an ABHA number (preferably with Aadhaar). Every ABHA number also automatically acts as a ABHA address on the NHA HIE-CM and looks like <14digitabha>@abdm
Users can create an ABHA address by downloading a PHR mobile application or on a portal provided by the HIE-CM. Use phr.abdm.gov.in to create a new ABHA address
Users can create an ABHA addresses in one of two ways:
- Using self declared information - This requires Name, Year of Birth gender along with a mobile number or email
- Using an ABHA Number - This requires users to first create an ABHA number with strong KYC
Note : While users are allowed to create more than one ABHA address, ABDM encourages every user to have only ONE ABHA address. The process of obtaining an ABHA address is designed to ensure that users don’t accidentally create multiple addresses
Try it out - Create an ABHA address that you can use on the ABDM sandbox at phrsbx.abdm.gov.in. This will create an ABHA address on the @sbx HIE-CM hosted within the sandbox
Use ABHA number for patients without phones
ABHA number is a 14 digit number that is unique (only one per person) issued only after a strong KYC. Every ABHA number is automatically available as an ABHA address on the NHA HIE-CM like <14digitabhano>@abdm. ABHA is a core building block of the ABDM ecosystem and integrates with several other systems to provide online KYC including Aadhaar, Driving licence and PAN
You can obtain an ABHA number by signing up at https://abha.abdm.gov.in
ABHA numbers are extremely important for helping those who use feature phones or do not use a phone to manage their personal health records. ABHA numbers are issued in assisted mode extensively by all Government health programs. Government programs are encouraged to link any health records they create to <14digitabhano>@abdm.
You can play around with the sandbox instance of the ABHA building block at https://abhasbx.abdm.gov.in
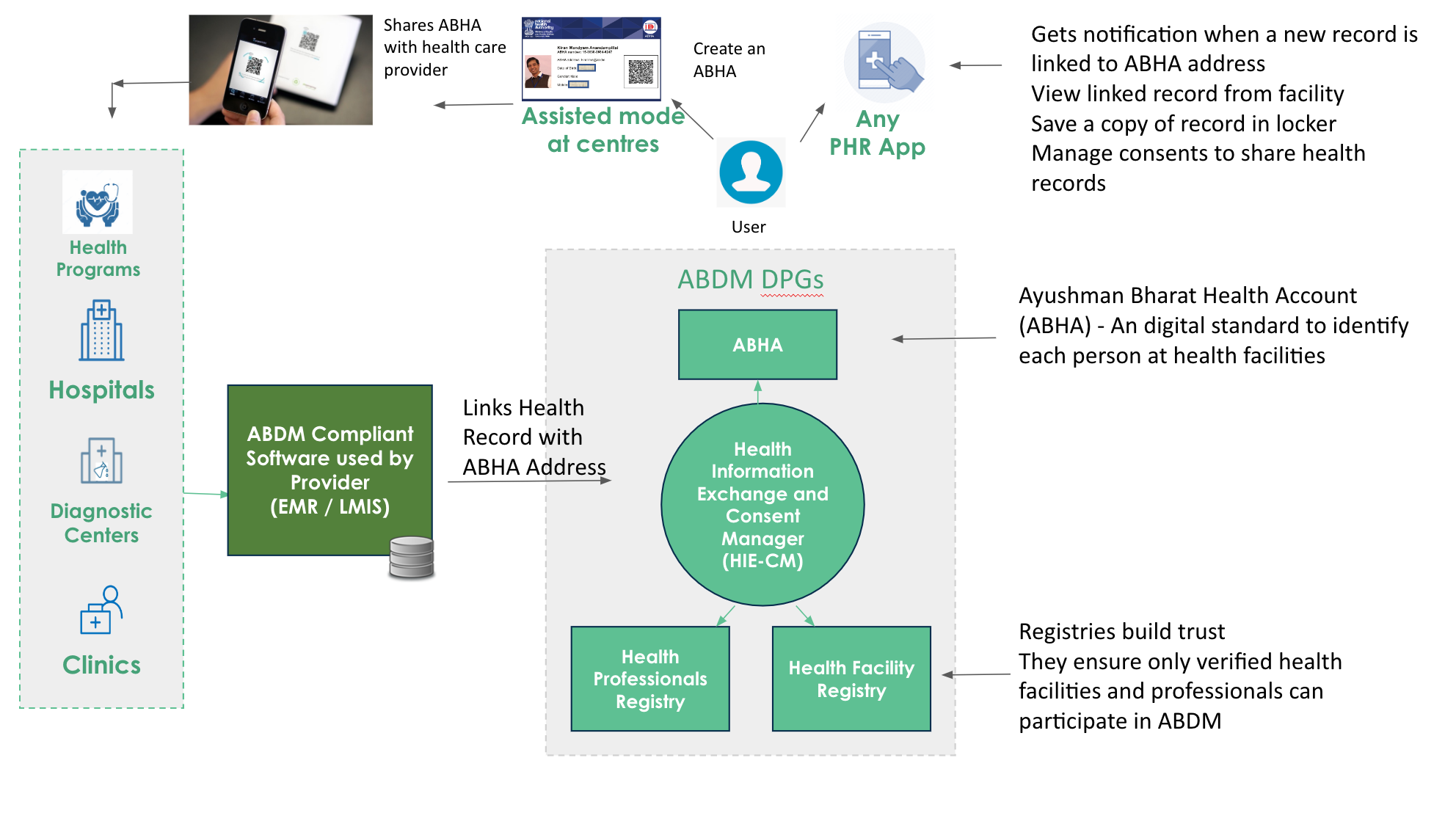
Health Information Exchange & Consent Manager (HIE-CM)
This is the key ABDM building block that manages ABHA addresses, maintains links to health data for each ABHA address and manages consents provided by the user for sharing of their health data. It also supports exchange of interoperable health data between HIPs and HIUs.
The ABDM architecture is designed to support multiple HIE-CMs to operate in the network. Each HIE-CM is referred to by a domain. NHA operates 2 HIE-CMs currently. A Sandbox HIE-CM with the domain @sbx and a production HIE-CM with the domain @abdm.
The diagram below shows how the HIE-CM orchestrates the linking of health records in ABDM.
Capturing ABHA address during patient registration
Health Facilities are required to modify their processes during patient registration to include the capture of ABHA address from patients. This is the primary area where a change management is required. All the other ABDM FHR related processes are in the background and do not require significant operational changes by the health facility.
ABHA address can be captured by the facility by any of the following methods
Scanning Health Facility QR code - Every health facility can create a QR code that can be displayed at their registration counter. Patients can scan this QR code from any PHR application. This “scan and share” action ensures that patient demograhics (including the ABHA address) is instantly shared from the PHR app to the ABDM compliant EMR / HIMS software being used by the health facility
Scanning the QR on the users ABHA card - Users without phones / feature phones can be issued a ABHA no and a printed ABHA card. This contains a QR code that can be rapidly scanned by the health facility using a 2D barcode scanner. It provides all the demographic information about the patient and also the ABHA address of the user
Verbally shared ABHA address - Users may share their ABHA address verbally during registration. Health facilities can verify the ABHA address and obtain the demographic details associated with the address by initiating an authentication request. This will result in an OTP being sent to the user which they can then share with the health facility
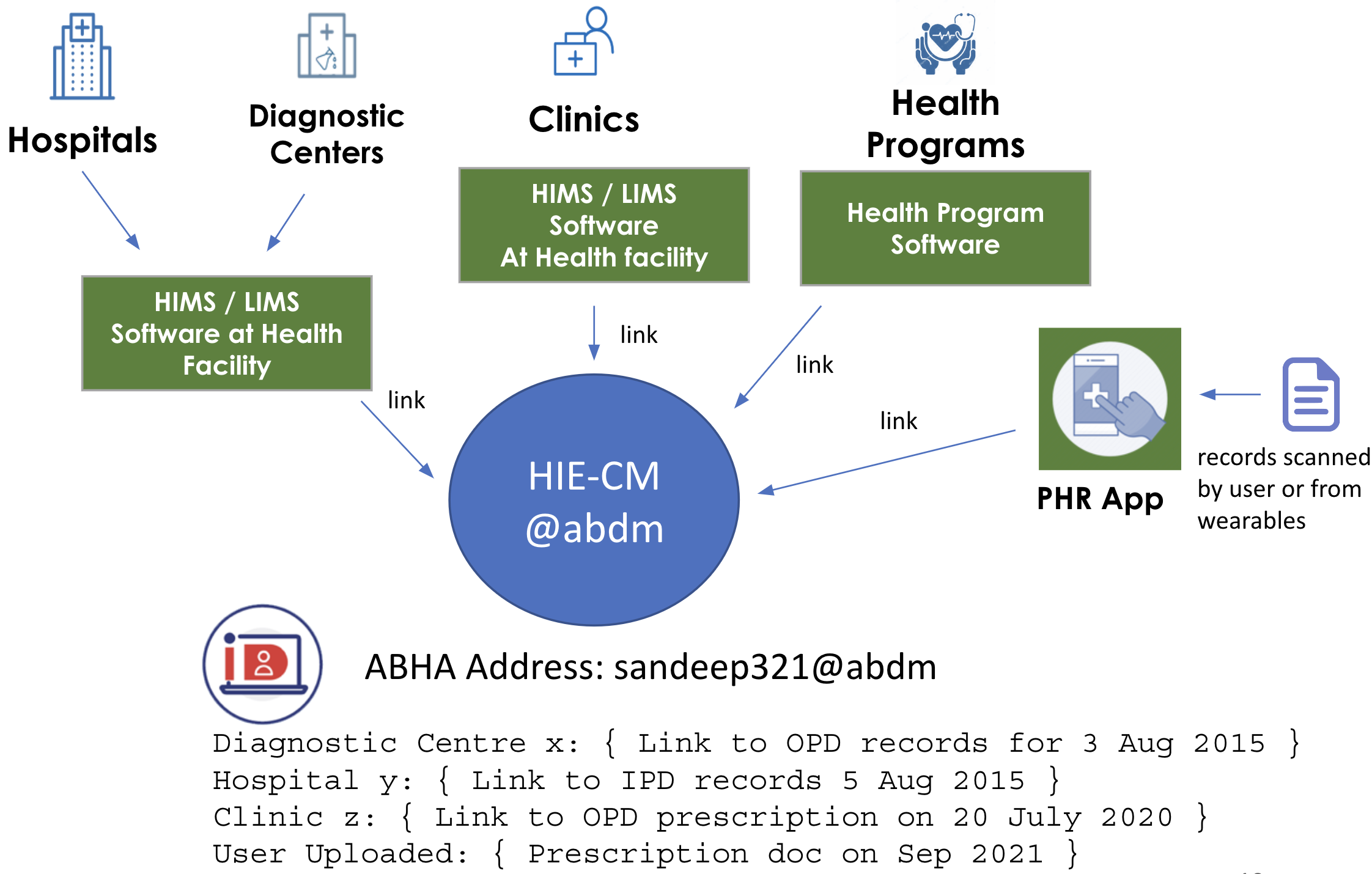
Linking of records by Health facility
If the patient has shared their ABHA address with the health facility, then the facility must link any new health record it creates to the ABHA address. Linking is done by adding a “Care Context” to the ABHA address. The care context only contains - a reference id to the actual health record and a display text that can be shown to the user. The display text should not contain any health information either. The FHR architecture is designed to ensure that the HIE-CM is “data blind”, ie does not have access to any health data of the patient.
Whenever a new care context is linked to a ABHA address, the HIE-CM notifies all PHR apps being used by the patient that a new care context has been linked (or updated). The PHR app will request for a copy of the health record from the HRP and display it to the user.
Discovery & linking of records by patients
Several patients may not have a ABHA address or share their ABHA address with the health facility at the time of registration. In such cases, the health facility will send an SMS the patient (via HIE-CM) that a new health record is available and can be accessed via any PHR app.
All PHR apps provide a “discovery” feature, where the user can search for a health facility and request for their health records. Users provide their name, year of birth, gender and mobile number as the parameters for this search. If there are records available at the health facility for this patient, the HRP will return a set of care contexts. All reocrds for the patient including historical records are expected to be provided via this method. The user can then link these discovered care contexts with their ABHA address using their PHR app.
Federated Health Records Architecture
ABDM is implemented as a Federated Architecture, where data is kept by the entity that generates the health data (HRP). The ABHA address only holds a set of care contexts which points to the health data across multiple HRPs. The HIE-CM is designed to be data blind, ie it does not know any details of the health records that are linked with the ABHA address.
The HIE-CM is also responsible for storing all consents provided by the user. ABDM uses a structured digital consent artifact that is based on the MietY consent framework. Each consent has a clear purpose of use, what type of records and from what period are being shared and how long the reciving entity (HIU) can keep / access these records. ABDM puts the user in control allowing them to easily grant, deny and revoke consents from their PHR app.
The HIE also allows health data to flow from HRPs to HIUs (with appropriate Consents). The health data is encrypted by the HRP so that only the requesting HIU entity can decrypt it. Also the design ensures the flow of data does not pass through the HIE-CM.
User generated health records like smart watches, home health monitors or even photos of health records can be linked to the ABHA address by PHR apps.
The FHR architecture is aligned with the upcoming Data Protection Bill. Any health facility using a ABDM compliant software would be able compliant to the provisions of the Data protection bill.
Summary of the FHR Architecture
- No central data repository
- Your ABHA Address only holds links to your health records
- Your Health record is held by Health Facility that generated the record
- You can get a copy of the record and save it long term using a PHR application
- You are in control of your health data and can decide what and whom you share it
- Even after your share, you can change your mind and revoke your consent at any time.
- You can also upload any health records by scanning them or even add data from your wearable devices to your health record via PHR apps
- Only verified health facilities that are part of the Health Facility Registry can link health records with your ABHA address
PHR applications & Health Lockers
Personal Health Record Applications are software service providers who offer web / mobile applications to individuals. ABDM is designed to have multiple PHR offerings as choice to user. Every PHR apps can
- Help users create an ABHA address
- Discover and link health records
- Help user grant / revoke consents
- Allow users to view their records
- Offer long term storage of records,
- Support uploading of users health records
- Share records on the ABDM network.
NHA has created the ABHA PHR application as a reference application. The Aarogasetu App has also been upgraded to become an ABDM compliant PHR App.
ABDM also rolled out a specification for a “Health Locker”. Lockers are entities that offer long term storage of health records to users. This functionality has been included in the requirements of a PHR application
You can play around with the sandbox instance of the ABHA PHR app at https://phrsbx.abdm.gov.in
What is an HIU?
An HIU (Health Information User) is an entity that wants access to the digital health information linked to a ABHA address. An HIU can be a hospital, clinic, PHR app, healthcare technology company, organizations working on health analytics, insurers, medical researchers, government entities etc. HIUs first need to collect a consent from the user and then can request for health records. HIUs get a copy of the patients records and use them only for the purpose specified in the consent and must delete them if the consent expires or is revoked by the user.
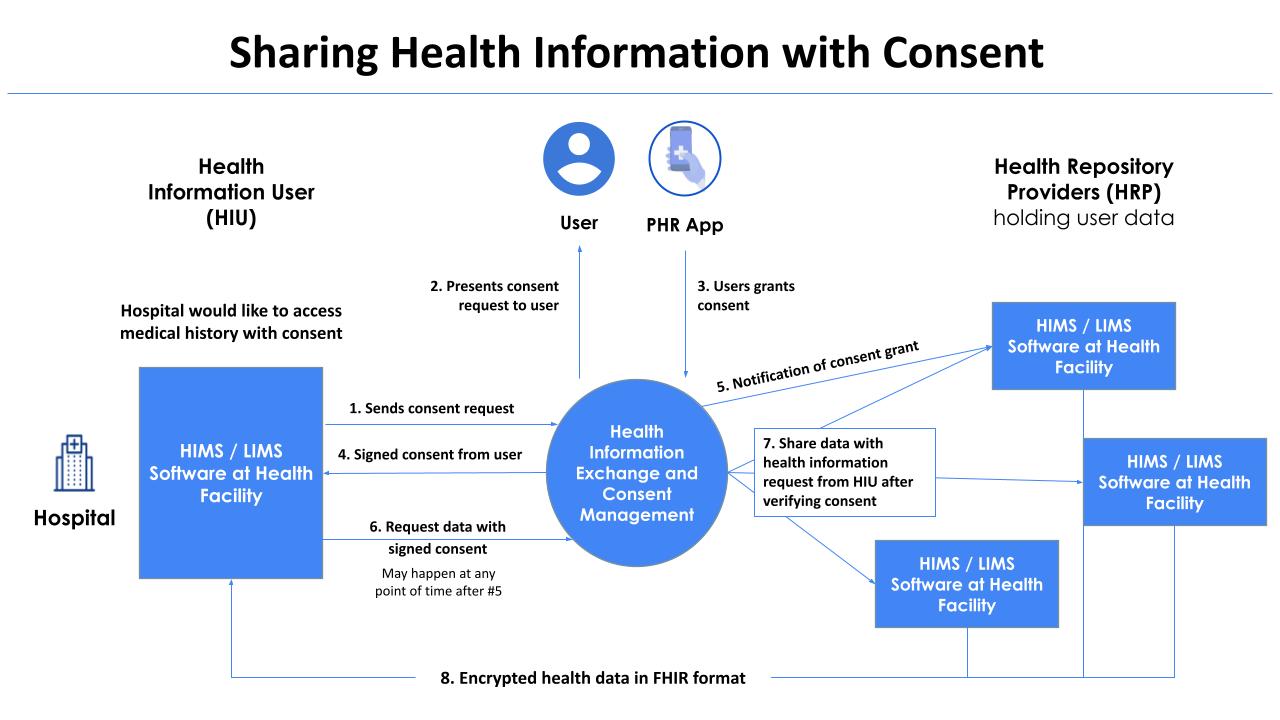
Sharing Health Records With Consent
- When any HIU wants to access records linked with a PHR address, it initiates a consent request with the HIE-CM
- The consent request consists of the purpose for which health records are being sought, why type of records are being sought, from what time period and how long will the HIU like to retain these records
- HIE-CM forwards the request to the user who can view the request on their PHR app and decide what he actually wants to share when he grants the consent
- User’s can also decide to revoke the consent anytime after it is granted
- If the user grants the consent, the HIE-CM shares a signed consent artificat with the the requesting HIU
- The HIU can now request for data for a ABHA address along with the signed consent artificat
- The HIE-CM forwards the request to all HRPs that are holding the linked data
- The HRPs verify the consent and push the data to the HIU
- Data has to be in the specified FHIR format to achieve interoperability
- Data is encrypted using a method that ensures only the requesting HIU can decrypt the data
Health Data Management Policy & HIP / HIU Guidelines
Any entity participating in ABDM will need to adhere to the Health Data Management Policy and the HIP/HIU Guidelines
This policy is a guidance document to set out the minimum standard for data privacy protection that should be followed by all the participants/stakeholders of the ABDM ecosystem. It is a first step in realizing ABDM’s guiding principle of “Security & Privacy by Design” for the protection of individual’s personal digital health data.
The Guidelines cover the responsibilities of Health Information Providers, Health Repository Providers, Health Information Users and Personal Health Records Apps
Digital Solution Companies must familizarize themselves with the Policy & Guidelines and ensure they support health facilities, consumers and health data users to comply with the same.
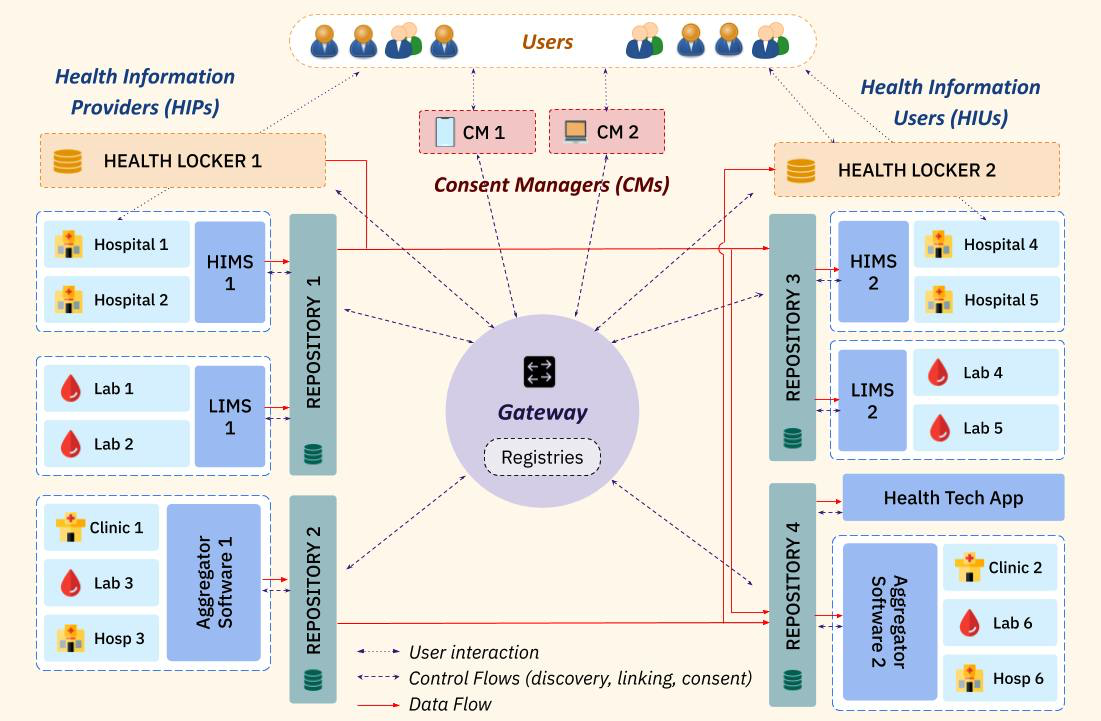
The ABDM Gateway
Gateway is the hub that mediates and connects HIE-CMs, Health Repository Providers and HIUs in the network. Its primary job is to allow for discovery, routing in the network. The gateway does the following:
- Connects and validates the HIE-CMs and health repositories (servicing HIUs and HIPs) to the network.
- Enables routing of information.
- Authenticates connected systems within the PHR network (provides a signed authentication token for further communication). The entire PHR framework including the gateway communicates via asynchronous APIs over HTTPs channel.
The following figure provides a view of how the Gateway fits in with other components

Experience PHR in action using the ABDM sandbox
ABDM provides a sandbox environment with core essential services that enable integrators who want to become HIPs/HIUs/HRPs or PHR apps build and test their integration.
Try out the following
- Create a PHR address on the sandbox from https://phrsbx.abdm.gov.in/
- Use EMRSBX to register your PHR address and link it with a new health record
- Download and login to the Sandbox PHR app with your new PHR address Download ABHA App
- Provide consent and view the health record you linked via EMRSBX
- Try adding your COVID vaccination record from CoWIN to your PHR address